- >
- BPM Software >
- Business Process Modeling: An Overview - Definition, Benefits and Examples
Business Process Modeling: An Overview - Definition, Benefits and Examples
When your CFO questions why the new automated approval workflow is taking longer than the manual process it replaced, or when departments blame each other for process breakdowns that no one can trace or fix, you're seeing the consequences of implementing technology without proper process modeling. As a technology leader managing enterprise systems, you face constant pressure to prove ROI while avoiding costly implementation failures. Forrester's 2024 Enterprise Architecture Report shows that organizations using formal process modeling reduce project failure rates by 45 percent and cut implementation costs by an average of $1.2 million per major system deployment.

See Kissflow in Action
Take a guided tour of Kissflow to build apps and automate workflows.
What is Business Process Modeling (BPM)?
Business Process Modeling (BPM) is the analytical representation and digital simulation of an organization's business processes, using standardized methodologies and tools to design, analyze, and optimize workflows before implementation, enabling data-driven decision-making and risk mitigation in process transformation initiatives.
Checkout: Best BPM Tools for Enterprise Business Process Management
Why Use Business Process Modeling?
Your first step in modeling is actually pen and paper. However, to actually run a business process, you will need to digitize that process in a way that a workflow engine can understand.
Business process modeling software allow you to represent your process in a digital way that can then be transferred to a live automated process.
There are many benefits to business process modeling:
- Gives everyone a clear understanding of how the process works
- Provides consistency and controls the process
- Identifies and eliminates redundancies and inefficiencies
- Sets a clear starting and ending to the process
Business process modeling can also help you group similar processes together and anticipate how they should operate. The primary objective of business process modeling tools is to analyze how things are right now and simulate how should they be carried out to achieve better results.
Business Process Modeling Techniques
Business process modeling can be expressed through flowcharts, programs, hypertext, or scripts. There isn’t just one way to implement business process modeling; in fact, you can choose from as many as 12 techniques.
Here are some of the most common business process modeling techniques:
1. Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN)
BPMN 2.0 has become something of a standard syntax used by process analysts and those who create business modeling tools. It is a relatively simple usage of lines, arrows, and geometric shapes that all communicate the flow and nuances of the process. A process consultant can look at a BPMN 2.0 model and know exactly how it should function.
“Eventually, when [those] companies get their products shipping and crank up their marketing machines, BPMN will be the unquestioned standard for process modeling and execution. But right now, we are still between the news and the reality.” - Bruce Silver, Process Consultant and Author of the book BPMN Method and Style
However, BPMN 2.0 is still a learned language, and although relatively simple, isn’t immediately intuitive for the regular business user. It is a great tool for process consultants, but not helpful for those looking to create their own applications.
2. Universal Process Notation
Instead of having a new language to learn, a more intuitive system is Universal Process Notation or UPN.
UPN provides a simple box for each task to be completed. The box shows what happens, who is assigned to it, and when it happens in the sequence. It is extremely useful for IT to design and analyze processes, for management to comply to business norms, and - more importantly - for end business users to understand processes as intended. Kissflow uses UPN in its modeler.
Learn more: Process automation solutions
3. Flowchart Technique
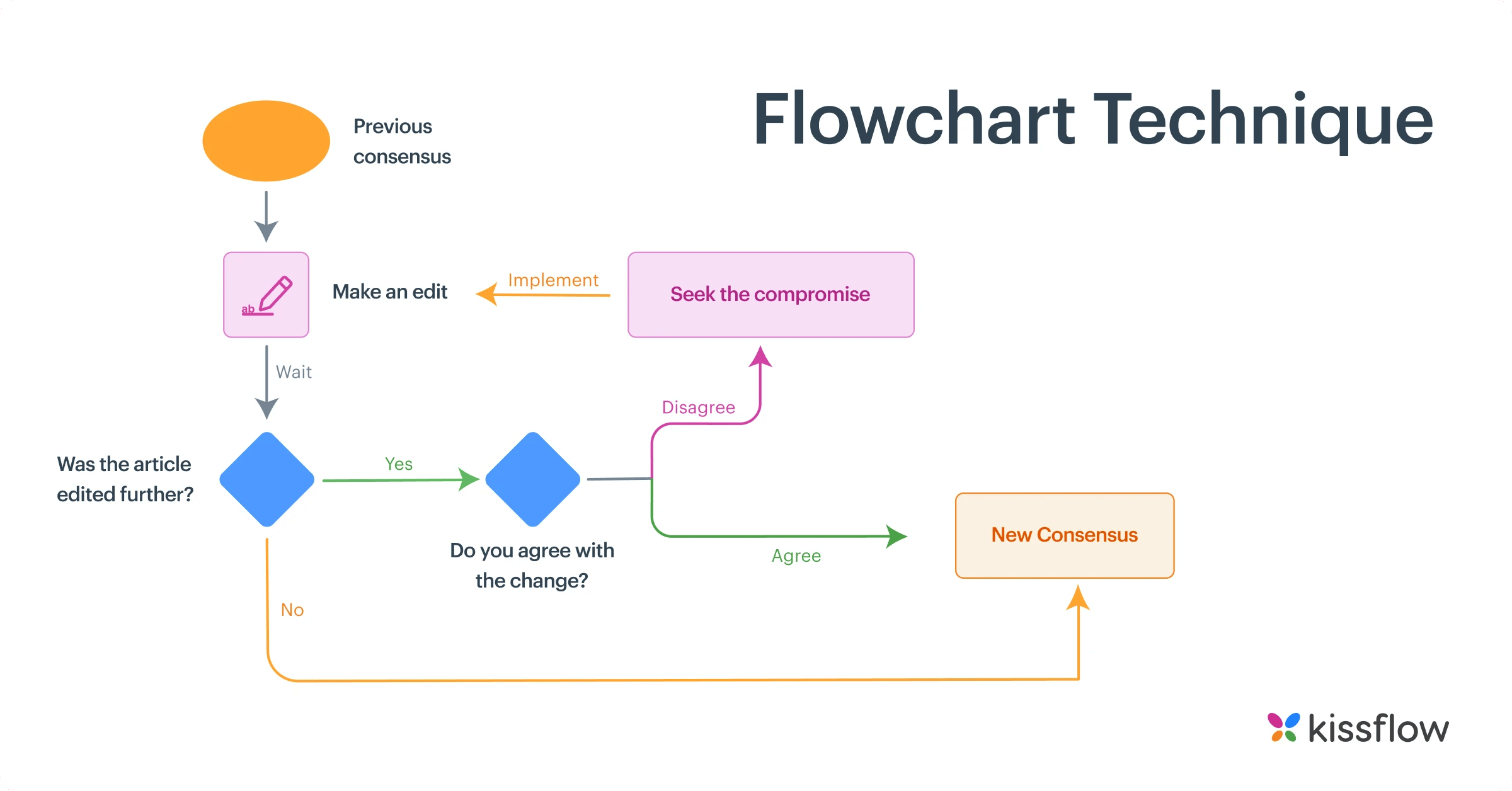
Flowcharts explain complex process flows in a simple yet effective way. They illustrates process steps in their sequential order, going from inputs to actual process to outputs. In fact, flowcharts provide the basic framework for BPMN to display advanced process flows.
Kissflow, our process tracking software, can help your business stay constantly aware of every last business process.
4. Gantt Charts
Rather than showing the steps sequentially, Gantt charts are able to show the entire process using ‘time taken’ as one of the main axes. It does a better job of showing the overall time taken to complete a project than other options.
5. Petri-Nets
Traditionally a modeling technique in mathematics, petri-nets are also useful for modeling business processes. Petri-nets classify or color-code complex workflow steps, users, and routes in different colors.
Learn more: Automation Technologies
What Do I Need in a Process Modeling Software?
Most BPM Suites include business process modeling tools in them. However, some have the modeler as a separate application.
The modeler is one of the most important elements in a BPMS, and you should spend a lot of time learning it before committing to buy a suite. Implementing effective Business Process Modeling can significantly enhance process efficiency. With business automation software, companies can unify fragmented processes, eliminate redundancies, and ensure consistent execution across departments. This creates a foundation for scalable operations and better decision-making at every level.
Great business modeling tools should:
- Be easy to learn for the business departments
- Be simple for IT teams to communicate with other departments
- Be inexpensive and industry compliant
- Have an integrated workflow editor tool with graphic interface
- Be able to simulate workflow before implementing
Learn more: Process automation solutions
Check out why these 6 BPM Software are at the top of the competition!
Case Study
The Challenge:
RENU Contracting and Restoration grappled with unreliable manual processes, difficulty managing complex tasks, and inefficient tracking of process issues. They needed a solution to transform their operations, increase productivity, and ensure accountability.
The Solution:
Michael Casamento, Director of Process and Procedure at RENU, discovered Kissflow during a web search. Impressed by its features, ease of use, and value for money, he implemented it. RENU began building workflows for check requests and merchandise returns. The success of these implementations led to the automation of other operations, such as claims processing, debit memo processing, and maintenance requests.
The Outcome:
Kissflow has become essential for managing many of RENU's critical processes. The company has experienced enhanced productivity, time-saving in process creation, increased accountability, minimal development time, and improved end-to-end trackability of processes. Michael praises Kissflow for its well-designed user interface and responsiveness to community input. Integrations with other apps via Zapier have further improved operations. Now, RENU looks forward to building an on/off-boarding process using Kissflow.
Learn more: Process building software.
Conclusion
Kissflow is a business process management platform that can be a game-changer for businesses. It allows organizations to visualize, analyze, and optimize their workflow in a user-friendly, low-code platform interface. This not only enhances productivity but also fosters improved collaboration and operational excellence. With its comprehensive and intuitive tools, Kissflow empowers CIOs and other business leaders to seamlessly align IT initiatives with broader business objectives, paving the way for strategic success in the ever-evolving landscape of technology and business. Solve your workflow challenges with Kissflow Platform and optimize your team's productivity.
FAQ's- Business Process Modeling
1. What is business process modeling and why is it important?
Business process modeling creates visual representations of how work flows through an organization. These models make abstract processes concrete, helping teams identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and improvement opportunities. Modeling establishes a common language between business and technical teams, facilitating clearer communication about process requirements. Models also serve as documentation for training and process standardization efforts.
2. How does BPMN improve process modeling?
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) provides a standardized visual language that bridges the gap between business and technical teams. Its formal notation eliminates ambiguity, ensuring everyone interprets processes the same way. BPMN models can be executed directly in BPM systems, turning diagrams into working applications. The notation supports simulation and analysis to identify bottlenecks before implementation. Perhaps most importantly, it's internationally recognized, facilitating communication across organizations.
3. What tools help with business process modeling?
Visual process designers with drag-and-drop interfaces make modeling accessible to business users. Simulation tools test process changes before implementation. Collaboration features enable team input throughout the modeling process. Version control tracks changes over time. The most advanced tools include AI-assisted modeling that suggests improvements based on performance data and industry benchmarks.
4. What industries use business process modeling?
Financial services rely on process modeling for compliance documentation and operational efficiency. Healthcare organizations model patient journeys to improve care coordination. Manufacturing companies use modeling to optimize production workflows. Government agencies model citizen service processes to reduce bureaucracy. Supply chain operations benefit from modeling complex multi-party processes that cross organizational boundaries.
5. How can I create an effective business process model?
Start by clearly defining the process purpose and scope – what triggers it and what successful completion looks like. Identify key stakeholders and gather their requirements through interviews and observation. Map the current state to understand existing flows before designing improvements. Use standard notation like BPMN to ensure clarity. Include exception handling for when things go wrong. Finally, validate the model with the people who actually perform the work.
Related Articles