80%[1] of workers say they have used SaaS applications at work without approval from IT. And that’s not all, 35% of employees say they disregard their company’s security policy to get their job done.
Shadow IT is a big problem and can topple a business. It also poses many risks—like security and regulatory non-compliance, inability to perform disaster recovery, and data leaks.
Shadow IT involves activities such as:
- Usage of unauthorized systems
- Occurrence of security gap
- Compromise of existing security software
These activities can lead to the breakage of firewalls which means hackers can easily access confidential company information.
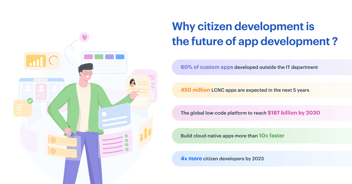
To combat shadow IT, many enterprises are turning to low-code, no-code application development platforms. Citizen development is one of the best-proven initiatives that can solve a range of business problems with ease and speed. It’s all about empowering business users to build apps using IT-approved tools.
What is shadow IT?

Shadow IT is the use of IT software, applications, systems, devices, and services without approval from IT. It has grown rapidly in recent years as organizations have adopted cloud-based applications and services. While it can drive innovation and improve employee productivity, it can also bring about serious security risks to organizations through compliance violations, data leaks, and more.
Why do IT managers struggle to manage shadow IT?
IT’s security efforts focus on protecting critical business operations and data. When unapproved and unmanaged tools are used to create applications, data is stored in low-trust environments. Using resources outside of IT bypasses procedures designed to properly document applications. Appropriate security requirements and testing may also be shunned.
Shadow IT can evade strong network and data access controls, elevating risk. In addition, the adverse impacts of non-compliance are high. App developers usually follow the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and other laws when creating apps, and employees seeking a quick solution might not care about these laws.
Threatening consequences of shadow IT

Security risks
Because shadow IT isn’t vetted by the IT department, the apps created don't follow the same security procedures as other supported technologies. And while some apps may seem harmless, they might share sensitive data.
When IT is in charge of the process, applications that put the company at risk of data breaches and other liabilities aren’t developed.
Non-compliance
Regulatory compliance has always been a concern for businesses in highly regulated industries. But it’s now a priority for every business due to laws like California’s Consumer Privacy Act and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).[2]
Shadow IT makes compliance difficult because IT is unable to apply the same risk-assessment measures it does for authorized applications. The apps can’t be audited to understand risks and to prove compliance. And in case an incident occurs, it’s difficult to identify the full scope and impact of a security event.
Data loss
Organizations can lose access to data when the person who owns the information leaves the company. For example, if an employee keeps customer contracts in their personal Dropbox account, the company may have difficulty getting the information back if the employee is terminated.
System inefficiencies
It’s inefficient to store and use data in multiple infrastructure locations. And if IT isn’t informed of data flows, it cannot plan for system architecture, security, performance, and capacity for siloed shadow IT apps. Reporting and analysis become complicated when numerous data versions exist in different unmapped locations.
Poor IT Visibility
If one business unit relies on a shadow IT application and it fails, the IT team won’t have the knowledge or documentation to fix it. Third-party applications that aren’t sanctioned by IT aren’t meant to be part of your infrastructure.
f IT lacks visibility into the tools that employees are using, it can’t ensure that sensitive data and resources remain within the organization.
Learn more: How Citizen Development Unites Business and IT
How Citizen Development Eliminates Shadow IT
Gives citizen developers a central platform
A citizen development framework makes IT aware of the citizen developers, their business units, and the tools they use. The IT team can govern how apps are developed and create a structure for adding citizen developers to the broader IT space. A citizen development strategy can help a business know its pressing needs.
Creates a centralized command center
There must be a centralized command center for citizen development where all app development activities can be monitored and managed. This team can be responsible for monitoring citizen development and ensuring that all activities follow the set regulations. It can also provide structure and resources to all citizen development activities.
Gives citizen developers important tools and resources
The key difference between shadow IT and citizen development is IT support. When citizen developers are given a platform to work from that IT can monitor, and the necessary training, they can develop enterprise citizen developer applications fast. About 77%[3] of IT decision-makers believe having an enterprise no-code platform can ensure citizen developers use the right data in their apps.
Makes app development secure
A no-code/low-code tool allows for continuous monitoring and training in data security adherence. When there’s a proper strategy and citizen development governance, the problems of shadow IT are eliminated. And because security features are built into cloud-based app development platforms, users can build custom apps that comply with prevailing regulatory requirements.
How to successfully implement citizen development
1. Train your citizen developers
Citizen developers must be well trained. They must have a deeper knowledge of things like information security, agile environments, and innovation programs to develop good applications. They must also be trained to use the app development platform. Training should be part of the citizen development journey. This will ensure they don’t revert to shadow IT. Training and guidance can help them create applications for their unique needs.
2. Control access
It’s important to keep things simple in terms of user access and the tools available to citizen developers. Unrestrained access can make citizen developers explore areas they don’t understand or know how to use, leading to security risks in the future.
Additionally, when citizen developers are given access to the full suite of tools, they may get overwhelmed or confused. The role of the employee should determine user access and tool selection. Access to more features can be given based on the task’s requirements.
3. Align business with IT
Citizen development enhances collaboration between business and IT. A no-code/low-code platform can ensure there are clear lines of communication between business users and IT. The IT department can establish usage policies for the users, creating a solid partnership that prevents shadow IT.
Learn more: How Does Citizen Development Facilitate Digital Transformation?
4. Monitor usage
The IT department must monitor what citizen developers are doing on the development platform. Monitoring user access, applications, and data can prevent security issues in the future. Data will be secure and business users will have the freedom to build applications that meet their requirements.
Citizen development - the future of application development
Shadow IT poses many business risks, but when IT oversight comes into the picture, non-technical staff build secure apps that comply with regulations. Citizen development allows business units to streamline processes and automate workflows without involving the IT team.
Organizations that implement citizen development programs future-proof themselves. Get Kissflow's citizen development platform and empower your citizen developers today.