- >
- BPM Software >
- The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a widely-used standard for modeling business processes. It provides a common language for businesses to communicate processes in a clear and consistent way, making it easier for teams to understand and improve their processes.
What is BPMN?
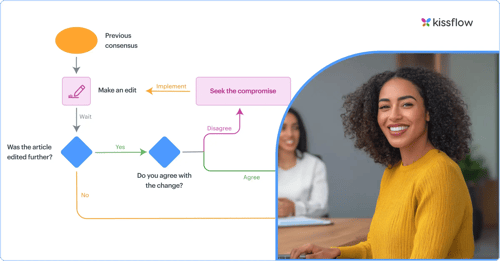
Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) is a graphical notation for specifying business processes in a process model. It is used to create diagrams that depict the flow of activities in a business process, from start to finish. The diagrams use a set of standard symbols to represent different types of process elements, such as tasks, events, and gateways.
Although process mapping has been widely used by many organizations already, it is often complex, confusing and there is no standardized way to implement it. There’s no single, unified procedure for documenting processes, so anyone who isn’t directly involved in the mapping process finds it hard to understand the maps. To eliminate this confusion, BPMN came into the picture.
BPMN is one of the most common business process modeling techniques and uses standardized symbols to make process maps easier to understand for all relevant parties: management, employees, and consultants. It offers a standard notation that’s readily understood by everyone. All parties can easily analyze public and private business processes.
BPMN helps companies and organizations:
-
Visualize business processes
-
Document processes
-
Analyze business processes
-
Discuss the processes using a common language

See Kissflow in Action
Take a guided tour of Kissflow to build apps and automate workflows.
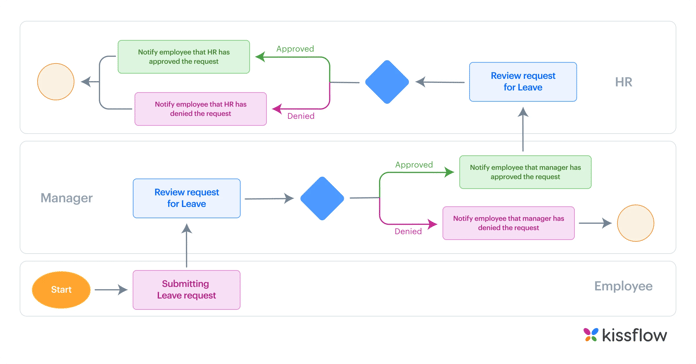
What’s the difference between BPM and BPMN
BPM (Business Process Management) is a discipline that utilizes different approaches to discover, analyze, measure, and improve business processes and help produce effective outcomes that support a business strategy. Business processes can either be structured or unstructured. Technologies are often used with BPM to align IT/OT investments to business strategy.
In simple terms, BPM methodology is effective for managing and controlling the processes in an organization and ensuring that they are streamlined to make an organization more cost-efficient. BPM allows organizations to align business functions with customer needs and also helps business executives determine how to deploy, monitor, and measure company resources. When properly implemented, BPM can boost efficiency and productivity, minimize costs, and reduce errors and risk, optimizing results.
Business process modeling notation (BPMN), on the other hand, is the pictographic language used to achieve the BPM tasks. A process map may describe a complex business procedure or a simple business process. Therefore, BPMN must be flexible enough to notate all business processes. This results in a language that’s easy to comprehend and relatively limited in scope.
In a nutshell, Business Process Management (BPM) is a methodology that analyzes and optimizes business processes to produce effective outcomes. Whereas Business process modeling notation (BPMN) is the pictographic language used to achieve BPM tasks.
Learn more: Process automation solutions
What’s the purpose of business process modeling notation?
The primary goal of BPMN is to support business process management for both business and technical users. It provides a notation that’s intuitive to business users but is also able to represent complex process semantics.
The BPMN notation models the steps of a planned business process from beginning to end. It is very important in Business Process Management because it visually portrays a detailed sequence of business activities and the information needed to complete a process.
A standard Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) helps organizations to understand their internal procedures visually and communicate the procedures in a standard manner. BPMN provides a notation that is easily understood by all parties involved, from business analysts (who create the initial drafts of processes) to technical developers (who implement the technology that performs the processes), to the employees (who use the technology).
BPMN examples
Example 1: Creating a bill
In this instance, we model a process in BPMN that uses some business rules. To create a bill, a discount may need to be added. The computed discount and the sum of the order are the relevant criteria to create a BPMN. The discount is computed before the bill is created and this results in a very simple process. The calculation of the discount itself shouldn’t be modeled in the BPMN.
Example 2: Credit check
Here, we model a process with concurring instances. If a credit check on a customer is already underway, we wouldn’t want another credit check to be performed for the same customer. This is because the different credit checks may influence the results. If one credit check is already running for a customer and there’s a request for another credit check, the new instance must check for concurring instances at the data level before initiating the second credit check.
Features of BPMN
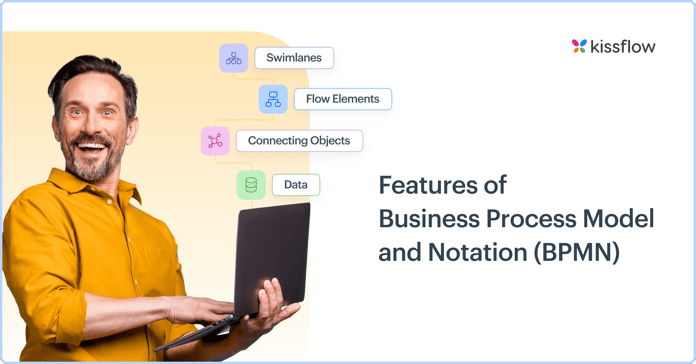
There are 4 basic categories of BPMN elements. Each represents a different aspect of a business process.
1. Swimlanes
These are graphical containers that represent the participants of a process. They are divided into pools and lanes.
2. Flow Elements
Flow elements connect to form business workflows. They define the behavior of a process and comprise events, activities, and gateways.
3. Connecting Objects
These connect the flow objects which unite to form a flow. They include sequence flows, message flows, and associations.
4. Data
This is the information needed or produced to execute a business process. It includes data inputs, data outputs, data objects, and data stores.
Types of BPMN Models
BPMN supports different model types based on the process scope and participant interactions. The three primary types are:
1. Private (Internal) Process
Used to model internal workflows within a single organization. It includes detailed tasks, events, and gateways but excludes external interactions.
Example: Employee onboarding process.
2. Abstract (Public) Process
Shows only the interaction (message flows) between an internal process and external parties, without revealing internal steps.
Example: Sending an invoice to a client.
3. Collaboration Process
Depicts how multiple participants (organizations or departments) interact using separate pools and message flows.
Example: Coordination between a supplier and a manufacturer.
Benefits of BPMN
BPMN allows an organization to capture and document business processes clearly and consistently, ensuring relevant stakeholders are involved in the process. That way, process owners can respond to any issues in the processes more effectively.
Business process modeling notation provides rich, comprehensive notations that can be easily understood by both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Here are 5 benefits it offers companies and organizations.
- It allows businesses to define and understand their procedures.
- It provides a standard notation that is easily understood by all company stakeholders.
- Helps bridge the communication gap that often occurs between business process design and implementation.
- It provides an industry standard by the OMG consortium.
- It excellently depicts the complexities of a business process yet is simple enough to understand.
BPMN is a great modeling notation for business processes. It gives more insight than flowcharts and is more understandable than UML Activity diagrams. It is also more suitable for process analysis and design. Solve your workflow challenges with Kissflow platform and optimize your team's productivity.
Kissflow BPM has a BPMN feature and can help your company to plot its business processes in a visual language that’s understood by all parties without misinterpretation. You can easily visualize and document business processes.
Frequently asked questions
1. How does BPMN help improve business efficiency?
BPMN provides a clear visual map of processes, helping businesses identify inefficiencies, reduce manual steps, and streamline operations for better productivity and cost savings.
2. What types of businesses benefit most from BPMN?
Enterprises with complex, repeatable, or compliance-driven processes—such as those in banking, insurance, healthcare, and manufacturing—gain the most from BPMN modeling.
3. Can BPMN support digital transformation initiatives?
Yes. BPMN acts as a foundation for process automation and optimization, making it a key tool in digital transformation strategies by aligning people, systems, and workflows.
4. Why should business teams adopt BPMN instead of traditional flowcharts?
BPMN offers standardized symbols and logic that can be understood by both business and technical teams, making it more robust than traditional flowcharts for process execution and automation.
5. How can BPMN align business and IT teams more effectively?
By using a shared visual language, BPMN helps business stakeholders define requirements clearly, which IT teams can then translate directly into executable workflows—reducing miscommunication and development rework.
6. What is BPMN and why is it important?
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) is a standardized graphical language for visualizing business processes. It's important because it creates a common visual vocabulary understood by business and technical stakeholders alike, eliminating ambiguity in process documentation. BPMN models can be directly executed in BPM systems, bridging the gap between process design and implementation.
7. How does BPMN improve process visualization?
BPMN improves process visualization through standardized symbols with precise meanings that eliminate ambiguity, clear representation of complex decision logic and exception handling, distinct swimlanes showing role responsibilities, visualization of parallel activities and dependencies, and the ability to show different abstraction levels from high-level overviews to detailed implementation views. This shared visual language facilitates communication across departments.
8. What are the best tools for BPMN modeling?
The best tools for BPMN modeling offer intuitive diagram creation with comprehensive symbol libraries, collaboration features for stakeholder input, simulation capabilities to test process changes, integration with execution platforms, version control for tracking changes, and analytics to identify potential improvements. Leading platforms combine modeling with execution capabilities in unified environments.
9. How does BPMN differ from traditional process mapping?
BPMN differs from traditional process mapping by using standardized symbols with precise meanings rather than generic shapes, explicitly showing different types of events and gateways, providing clear notation for exception handling, incorporating message flows between organizations, supporting multiple levels of abstraction, and enabling direct execution in BPM systems rather than serving purely as documentation.
10. What are common BPMN symbols and their meanings?
Common BPMN symbols include events (circles indicating something happens), activities (rounded rectangles showing work performed), gateways (diamonds representing decisions), sequence flows (solid arrows showing order), message flows (dashed arrows showing communication between participants), pools (representing organizations), and lanes (representing roles within organizations). These create a comprehensive visual vocabulary for process representation.
Discover BPMN with Kissflow
Related Articles




%20(1)%20(1).png?width=1997&height=1800&name=The%20ultimate%20buyers%20guide%20to%20BPM%20(1)%20(1)%20(1).png)
