There are multiple concepts in life that almost sound the same but are entirely different. Differentiating between them is quite important because of the high stakes involved. For example, Highschool students often feel confused about the difference between concepts like energy and power while grownups often find it hard to differentiate between cold and flu.
Some Agile methodologies like Kanban methodology make use of two such terms that are quite different yet similar enough to cause confusion. In lead-time vs cycle time, there is no doubt that a huge overlap exists. The ending point for both concepts is the same as well. However, what they represent is not.
Understanding lead time and cycle time is quite important because they are highly useful parameters and controlling them can have a significant effect on your overall productivity.
Before we start talking about how to effectively manage them for increased efficiency, let’s first understand what lead and cycle time really are and how are they different from each other.
What is Lead Time?
Lead time can be best described as the time span from the moment a task enters the work system to the point it gets completed. Lead time is essentially the time it takes for the input to move through all the operations to the finish line. In Kanban terms, the total time taken for the delegated task to reach the right-most column.
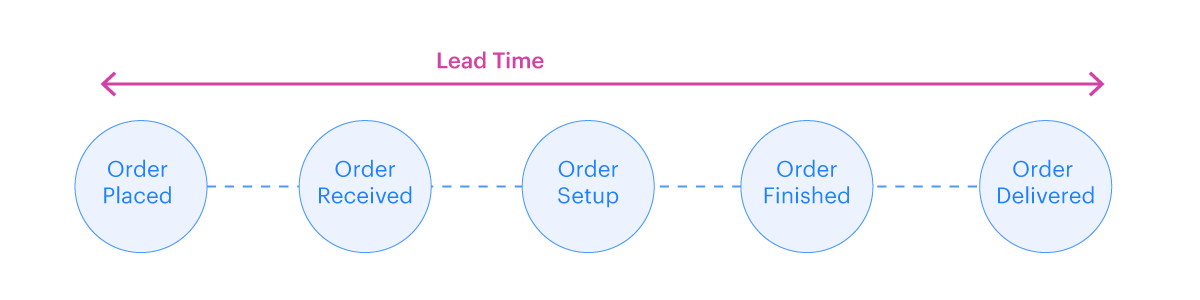
To understand it in a simpler way, imagine ordering a pizza. The amount of time it takes from the moment you ordered the pizza to when you get it delivered is defined as the lead time. So, if you placed the order at 8 and got the pizza at 8:30, your lead time would be 30 minutes.
What is Cycle Time?
Cycle time indicates how much time is devoted by the team to work on a prioritized task. The moment any team member starts working on the task and moves it to the ‘in progress’ column, cycle time starts and continues till the completion.
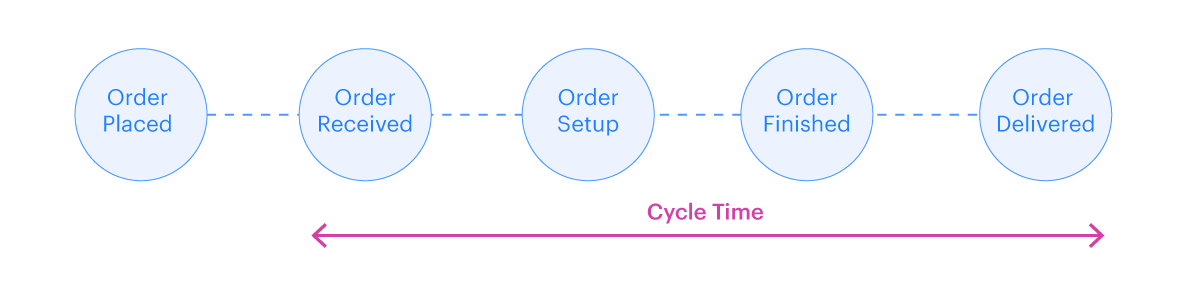
Continuing on the pizza analogy, the lead time begins the moment you finish placing your order. But the kitchen hasn’t received the order yet. The cycle time starts only when the cook starts working on your order. If the pizza order in the previous section took ten minutes to process and got received by the kitchen at 8:10, your cycle time would be 20 minutes.
Here is our Customizable Marketing Templates to try for Free:
– Marketing Plan Template to Streamline your Marketing Efforts
– Social Media Calendar Template for Social Media Planning
Relationship between Lead Time and Cycle time
The most important yet the most ignored difference between cycle time and lead time is their units of measurements. Lead time is measured in elapsed time (weeks, hours, seconds) while Cycle time has the unit “amount of time per unit/process/task.”
The relationship between Cycle time and Lead time is best described by Little’s Law which states:
Lead time = Cycle time x WIP (Work-In-Progress)
How to calculate Lead time vs Cycle time
Calculating the lead time and cycle time of any project is extremely easy if you have access to the right project management software and have all the information. The most convenient and commonly used way of calculating both lead and cycle times is through the Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD).
In basic terms, CFD is a graph depicting the progress of the project by mapping it on a graph. The vertical axis shows the WIP units while the horizontal axis indicates the time. The CFD is divided into different segments and each segment shows a single column of a Kanban board. Just like in the Kanban board, the three basic segments are planned tasks, tasks in progress, and completed tasks. However, you can add many more sections to further streamline the progress.
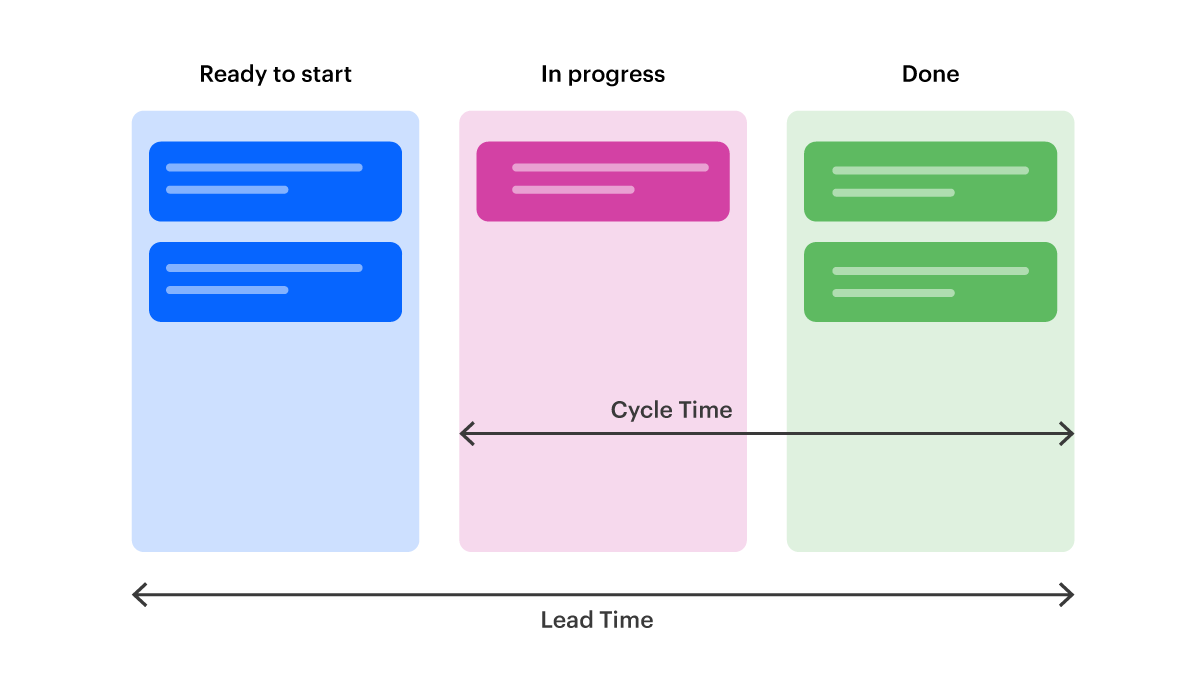
To calculate Lead time, you just need to interpret the data from the point a request is entered into the system (backlog), goes through the process (in-progress) and reaches the end to the point of completion (completed). The timespan for this dataset represents the Lead time.
On the other hand, calculating cycle time requires you to skip the initial phase when the item was in the backlog and consider the time after work is started. It is also important to note that cycle time is measured as time spent per unit.
Tired of using Asana?
See why Asana is not efficient to manage projects and why you need a Asana Alternative.
Benefits of calculating Lead time and Cycle time
The importance of calculating lead time and cycle time can help you understand the dynamics of your workflow. By definition, it’s not hard to know that in order to increase productivity, efficiency, reduce cost, and having the ability to outpace the competition, Lead time and Cycle time should be reduced as much as possible. The relation between these metrics and customer satisfaction is as direct as it gets.
In the manufacturing industry, the concept of Just in Time (JIT) relies on reduced lead time. The fact that many top-tier manufacturing and processing organizations rely on it proves the effectiveness of JIT. All organizations aim to maximize their profits by cutting the overall costs and by minimizing inventory. Lead time also plays an important part in estimating the demand.
Similarly, cycle time is also an important metric to calculate the efficiency of a process and to understand how much time has been “invested” in a single unit.
Based on the Cycle time of a process, we can calculate the amount of time it takes per unit and the worth of the process based on how much value that step actually adds to the whole product. This information can be particularly helpful to decide the worth of individual processes and to highlight any inefficient process.
Once known, the team can focus on optimizing that particular process which will obviously increase the overall efficiency.
–> Thinking about how to manage your self-organizing teams? Here’s the list of productivity hacks to help you better manage remote work.
Final takeaway
The benefits of controlling and reducing both lead and cycle times are immense. Their knowledge can greatly help in planning and improving the overall performance of a business.
However, in order to do that effectively, it is important to completely understand the differences between lead time and cycle time. Only then. they can be used in the most advantageous way for a business. Start using the Kissflow Platform today to enhance your project management efficiency.
Build Your Apps with Kissflow Low-Code Platform
Worried about how to manage your growing list of projects?
We have built a FREE solution. Just for you.
%20(2).png?width=2000&name=PSE%20Dashboard%20(3)%20(2).png)
.png?width=2000&name=Dashboard%20(5).png)