- >
- Citizen Development >
- Citizen Developer vs Professional Developer: Everything you need to know
Citizen Developer vs Professional Developer: Everything you need to know
Team Kissflow
Updated on 23 Apr 2025 • 5 min read
Many businesses are on the fence about citizen developers, even though 60% of all apps are now built outside the IT department. Starting a citizen development program makes a lot of sense because many companies lack the IT resources they need to implement digitization projects. Professional developers have always handled software development, but they are in short supply and often prefer hi-tech jobs—making it impossible for traditional businesses to hire them.
Citizen development has grown rapidly because organizations have realized that professional developers have too much responsibility–they have to manage existing applications, create new applications, and carry out digitization projects. In many companies, citizen developers have taken over app development. Let’s look at the differences between citizen developers and professional developers.
Who is a Professional Developer?
A professional developer is a person with the ability and expertise to create, maintain, and upgrade software for commercial purposes through coding language. They come from a coding background, understand the core concepts of product development, and are usually employed to use their knowledge in coding to create and develop apps.
Who is a Citizen Developer?
A citizen developer is an individual who can create custom applications for themselves, fellow employees, and customers. They have little to no coding knowledge and work outside the IT department. 61%[1] of corporations have already implemented citizen development projects or plan to.
Citizen developers use low-code/no-code platforms with visual interfaces and drag-and-drop builders to connect components and create software without writing code. In large enterprises, citizen developers have become so popular that by 2023, Gartner predicts that they will outnumber professional developers by four to one.
Learn more: What does Gartner say about citizen development and why should you care?
.webp?width=260&height=260&name=CD%20Cover%20-%20Mockup%20(2).webp)
Leader's Guide to Citizen Development
Thank you for Downloading
The Increasing Burden on Professional Developers
In years gone by, organizations highly depended on IT to create new applications and keep them functioning optimally. But endless requests for new apps meant IT could never keep pace with the demand. Additionally, some IT departments had limited resources to meet the many solution requests.
It's almost impossible for one department to fully operate in a fast-paced business environment and meet the ever-changing needs of employees and customers. This results in a backlog of work—projects requiring IT’s attention get stalled for months or more. In an effort to create apps faster and reduce developer backlogs, companies have started empowering citizen developers.
80%[2] of organizations believe citizen developers have given their IT departments more breathing room. Citizen development reduces backlogs, speeds up application development, and increases transparency and resource sharing. It allows IT to prioritize complex business projects.
Differences Between Citizen Developers and Professional Developers
| Professional Developers | Citizen Developers |
|
Can operate across a variety of departments. |
Are more well-versed in their specialty and build software that reflects their department or user needs |
|
Use complex programs and require highly-skilled coding infrastructure |
Use low-code or no-code systems with a simple graphical interface that enables them to build solutions without coding |
|
Have in-depth knowledge of IT and programming |
Have limited IT and programming knowledge. |
|
Projects are dependent on the availability of IT resources |
Projects are less dependent on IT resources |
|
Slower decision-making because of huge dependency on the business environment |
Faster decision-making because developers are involved from development to deployment |
The Benefits Citizen Developers Offer Via No Code Platforms
The benefits of implementing citizen development in an organization by the citizen developers are as follows.
Increased Productivity
When an IT department isn’t overwhelmed, productivity increases significantly. Organizations can design, build, and deploy applications in days or weeks instead of months. Citizen development lets IT focus on more critical issues like core system extensions, enterprise-wide applications, and legacy modernization.
Faster App Development
In a fast-changing business environment, speed is imperative to success. When IT is unable to deliver new solutions on time, 62% of forward-thinking employees get frustrated. Using low-code/no-code platforms to build apps cuts development time by 50%-90%.
Higher Employee Motivation
Equipping employees with the tech skills required to create enterprise apps boosts their motivation. They create digital tools based on their needs and feel empowered because they solve business problems and improve processes.
Reduced Costs
You’ll pay upwards of $28,584 to hire a top-notch developer for your organization. That’s why 84% of organizations use low-code/no-code tools to reduce the strain on IT. Also, thanks to citizen development, companies are hiring fewer developers and saving millions of dollars. Citizen development also allows employees to share resources and tools, minimizing costs.
Promotes Collaboration
In days gone by, software development was left to IT—the IT department didn’t collaborate with other departments. Low-code/no-code tools promote collaboration by uniting disjointed teams with a common goal. Non-IT employees without coding and programming knowledge can collaborate with the IT department and develop applications that fully meet the company’s needs.

Get The ultimate buyer’s guideto BPM software
Thank you for reaching us!
Thank you for reaching us!
The Life Cycle of Citizen Development
The life cycle of citizen development takes place in 4 stages.
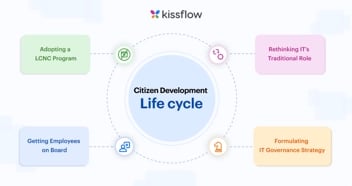
Rethinking IT’s Traditional Role
An organization that wants to adopt citizen development begins by redefining the IT department’s role. Its IT team stops building simple apps and focuses on managing IT infrastructure and building complex software.
Adopting a Low-Code/No-Code Program
The organization then gets a low-code/no-code platform to empower non-IT employees to create apps. They use the platform to speed up app deployment, reduce strain on IT resources, and drive digital transformation.
Getting Employees on Board
The organization builds a citizen development framework that empowers non-IT employees to build software using the low-code or no-code platform. By using an IT-sanctioned platform, citizen developers align business and IT. They create business-specific software without relying on IT.
Formulating IT Governance Strategy
IT establishes a strategy for overseeing citizen development that includes training, centralized oversight, and security reviews. Without IT governance and permissions, citizen developers cannot build, maintain, or upgrade software.
6 Tips to Successfully Deploy the Citizen Development Model
1. Create the Right Culture
Encourage your employees to experiment with technology and take risks. This cultivates the atmosphere of innovation every business needs to succeed. Encourage your employees to share their ideas and try to come up with solutions to their problems. Motivated employees are more likely to share unique solutions.
2. Select the Right Ideas
For the citizen development model to succeed, an organization must select actionable and viable ideas. And whatever ideas are picked, design-led thinking must be used to drive business growth and organizational efficiency.
3. Choose a Low-Code/No-Code Platform
The market is filled with low-code/no-code tools, but only one may be ideal for your organization. Picking the right one firstly hinges on how easy the platform makes it for non-IT teams to build citizen developer apps. Choose a secure platform with all the features your business needs that also fit your budget.
4. Train Your Employees
Citizen developers typically have moderate tech skills and an in-depth understanding of business processes, application infrastructure, and data. They are interested in learning app development but might need the training to build useful applications. Provide adequate training on organization-specific needs and assess their proficiency through basic testing.
5. Provide Guidance
To succeed, monitor the app development process and create guardrails for your citizen developers. This reduces errors and costly mistakes. Guide them on application development, approval processes, compliance, security, and testing methodology. Before building an app, citizen developers should know whom the app is for, its purpose, and the desired results. Their proposed solutions should fit into existing business objectives.
6. Inspire Collaboration
If citizen developers work alone, they will make costly mistakes. And without IT governance, they may create faulty apps or develop duplicate apps. Create a collaborative environment and clearly outline the tasks for IT and citizen developers. Citizen developers should be closely governed by IT and follow the best practices for citizen development.
It’s Time to Adopt Citizen Development
Your organization can speed up digital transformation and save valuable time and money with citizen development. Kissflow's citizen development platform helps companies like yours reduce the dependence on IT professionals and empower citizen developers to create the applications they need to drive efficient processes and boost productivity.
Kissflow is a no-code work platform that allows you to do more work within a single platform. It bridges the gap between business users and IT teams while truly embracing the philosophy of simplicity.
Related Articles











